ONNX Runtime Execution Providers
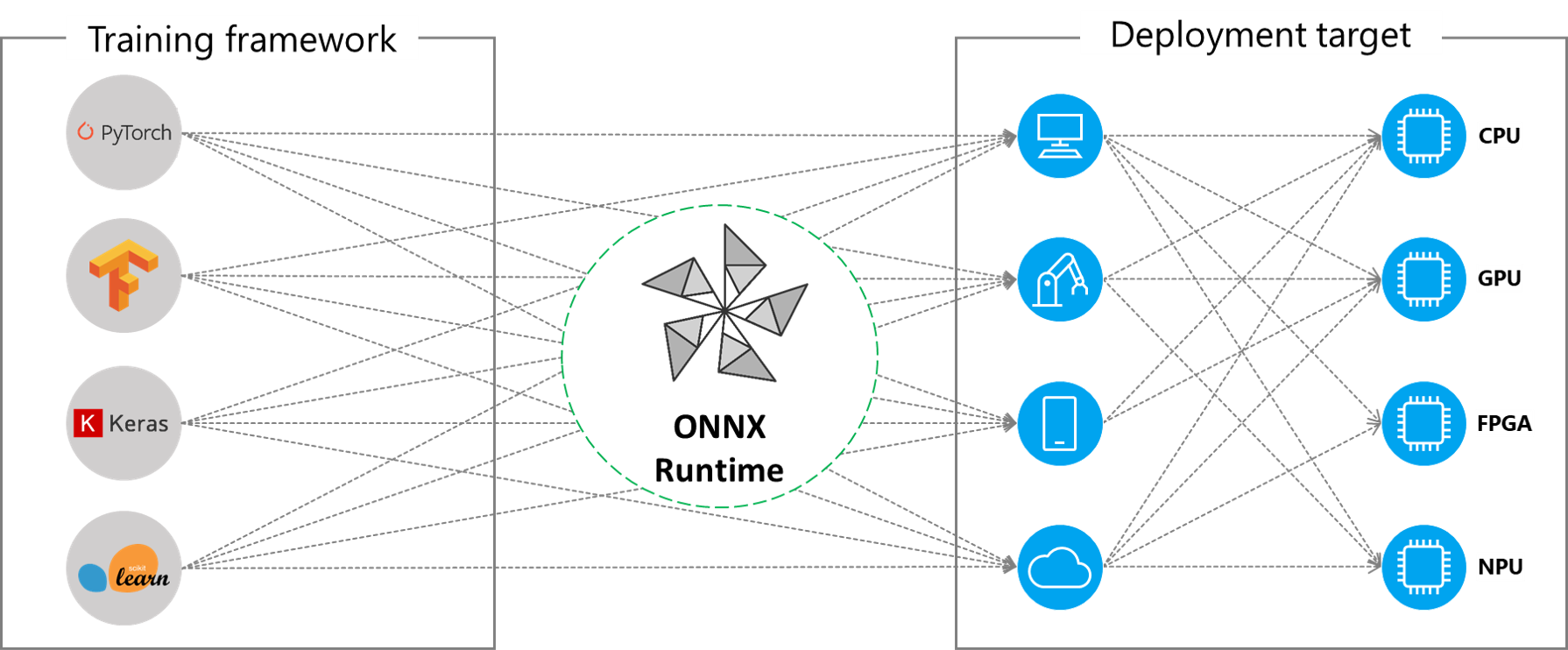
ONNX Runtime works with different hardware acceleration libraries through its extensible Execution Providers (EP) framework to optimally execute the ONNX models on the hardware platform. This interface enables flexibility for the AP application developer to deploy their ONNX models in different environments in the cloud and the edge and optimize the execution by taking advantage of the compute capabilities of the platform.
Onnx Runtime
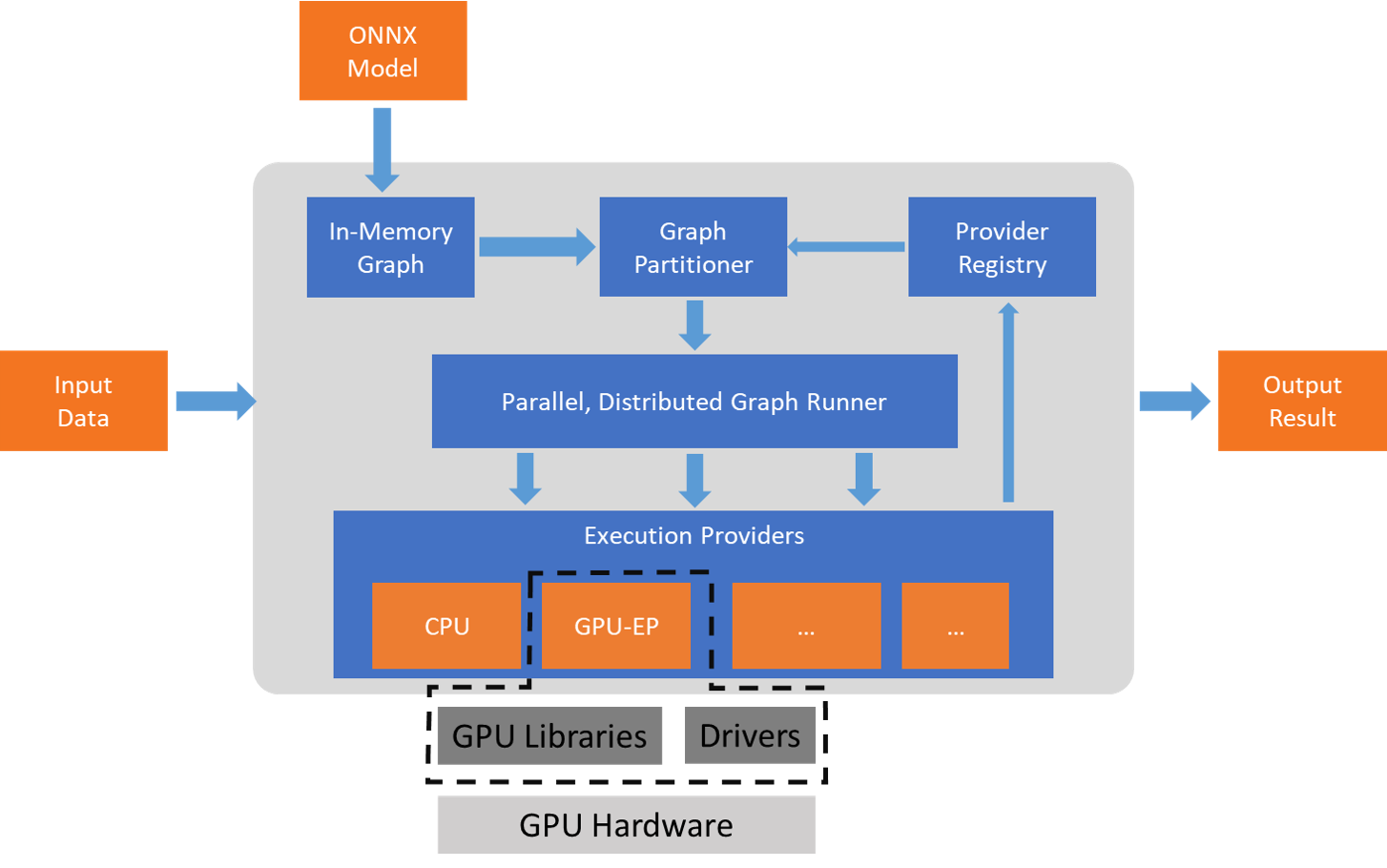
ONNX Runtime works with the execution provider(s) using the GetCapability() interface to allocate specific nodes or sub-graphs for execution by the EP library in supported hardware. The EP libraries that are pre-installed in the execution environment process and execute the ONNX sub-graph on the hardware. This architecture abstracts out the details of the hardware specific libraries that are essential to optimize the execution of deep neural networks across hardware platforms like CPU, GPU, FPGA or specialized NPUs.
Onnx Model
ONNX Runtime supports many different execution providers today. Some of the EPs are in production for live service, while others are released in preview to enable developers to develop and customize their application using the different options.
Contents
Summary of supported Execution Providers
| CPU | GPU | IoT/Edge/Mobile | Other |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default CPU | NVIDIA CUDA | Intel OpenVINO | |
| Intel DNNL | NVIDIA TensorRT | ARM Compute Library (preview) | Rockchip NPU (preview) |
| TVM (preview) | DirectML | Android Neural Networks API | Xilinx Vitis-AI (preview) |
| AMD MIGraphX (preview) | ARM-NN (preview) | ||
| TVM (preview) | CoreML (preview) | ||
| TVM (preview) |
Add an Execution Provider
Developers of specialized HW acceleration solutions can integrate with ONNX Runtime to execute ONNX models on their stack. To create an EP to interface with ONNX Runtime you must first identify a unique name for the EP. See: Add a new execution provider for detailed instructions.
Build ONNX Runtime package with EPs
The ONNX Runtime package can be built with any combination of the EPs along with the default CPU execution provider. Note that if multiple EPs are combined into the same ONNX Runtime package then all the dependent libraries must be present in the execution environment. The steps for producing the ONNX Runtime package with different EPs is documented here.
APIs for Execution Provider
The same ONNX Runtime API is used across all EPs. This provides the consistent interface for applications to run with different HW acceleration platforms. The APIs to set EP options are available across Python, C/C++/C#, Java and node.js.
Note we are updating our API support to get parity across all language binding and will update specifics here.
`get_providers`: Return list of registered execution providers.
`get_provider_options`: Return the registered execution providers' configurations.
`set_providers`: Register the given list of execution providers. The underlying session is re-created.
The list of providers is ordered by Priority. For example ['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider']
means execute a node using CUDAExecutionProvider if capable, otherwise execute using CPUExecutionProvider.
Use Execution Providers
To learn more about different Execution Providers, see Reference: Execution Providers.
Build the Execution Provider
ORT can be customized by building with different Execution Providers in different programming languages.
Python
Official Python packages on Pypi only support the default CPU Microsoft Linear Algebra Subprogram (MLAS) and default GPU (CUDA) execution providers. For other execution providers, you need to build from source. The recommended instructions build the wheel with debug info in parallel.
For example:
DNNL: ./build.sh --config RelWithDebInfo --use_dnnl --build_wheel --parallel
CUDA: ./build.sh --config RelWithDebInfo --use_cuda --build_wheel --parallel
C and C#
Official releases on Nuget support default (MLAS) for CPU, and CUDA for GPU. For other execution providers, you need to build from source. Append --build_csharp to the instructions to build both C# and C packages.
For example:
DNNL: ./build.sh --config RelWithDebInfo --use_dnnl --build_csharp --parallel
CUDA: ./build.sh --config RelWithDebInfo --use_cuda --build_csharp --parallel
Register the Execution Provider
Registering the ORT Execution Provider can be done in C, C#, and Python.
C API Example:
In order to use DNNL, CUDA, or TensorRT execution provider, you need to call the C API OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider.
const OrtApi* g_ort = OrtGetApi(ORT_API_VERSION);
OrtEnv* env;
g_ort->CreateEnv(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "test", &env)
OrtSessionOptions* session_option;
g_ort->OrtCreateSessionOptions(&session_options);
g_ort->OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(sessionOptions, 0);
OrtSession* session;
g_ort->CreateSession(env, model_path, session_option, &session);
C# API Example:
SessionOptions so = new SessionOptions();
so.GraphOptimizationLevel = GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_ENABLE_EXTENDED;
so.AppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(0);
var session = new InferenceSession(modelPath, so);
Python API Example:
import onnxruntime as rt
so = rt.SessionOptions()
so.graph_optimization_level = rt.GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_ENABLE_ALL
session = rt.InferenceSession(model, sess_options=so, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])
Here are some steps to set the execution providers for your Onnx Runtime.
import onnxruntime as rt
#define the priority order for the execution providers
# prefer CUDA Execution Provider over CPU Execution Provider
EP_list = ['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider']
# initialize the model.onnx
sess = rt.InferenceSession("model.onnx", providers=EP_list)
# get the outputs metadata as a list of :class:`onnxruntime.NodeArg`
output_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
# get the inputs metadata as a list of :class:`onnxruntime.NodeArg`
input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
# inference run using image_data as the input to the model
detections = sess.run([output_name], {input_name: image_data})[0]
print("Output shape:", detections.shape)
# Process the image to mark the inference points
image = post.image_postprocess(original_image, input_size, detections)
image = Image.fromarray(image)
image.save("kite-with-objects.jpg")
# Update EP priority to only CPUExecutionProvider
sess.set_providers(['CPUExecutionProvider'])
cpu_detection = sess.run(...)
Table of contents
- CUDA
- CoreML
- Arm NN
- ARM Compute Library (ACL)
- DirectML
- AMD MIGraphX
- NNAPI
- TVM
- Intel oneDNN
- OpenVINO
- RKNPU
- TensorRT
- Vitis AI
- Add a new execution provider